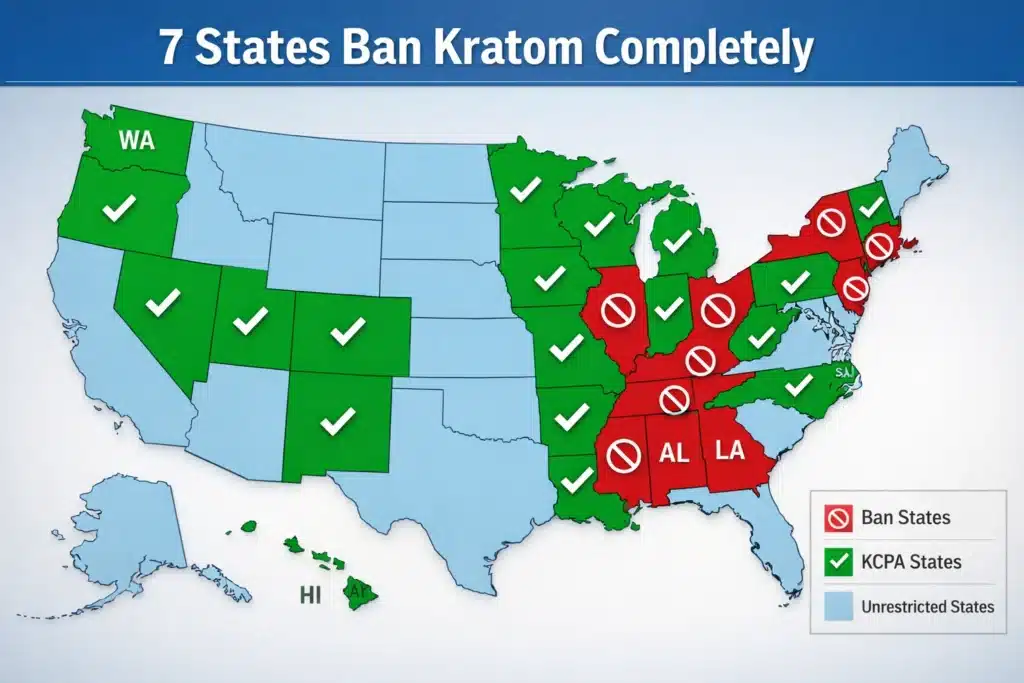
Kratom laws change fast. One state bans it completely. Another regulates it strictly. A third allows it freely. In 2026, kratom legal states create a complex patchwork across America. Seven states ban kratom outright. Twenty-four states regulate it with consumer protection laws. The rest? Legal but unregulated. Understanding where kratom is legal matters more than ever.
The landscape shifted dramatically in 2025. Louisiana banned kratom in August. Georgia tightened regulations in January. Rhode Island prepares to reverse its ban. These changes affect millions of kratom users. They impact where you can buy. They determine what you can possess. They define legal consequences.
- Seven states ban kratom completely as of 2026: Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Louisiana, Vermont, Wisconsin, and Rhode Island (plus Washington D.C.)
- Twenty-four states enforce consumer protection laws with age restrictions, testing standards, and alkaloid concentration limits
- Local bans exist within legal states, creating a patchwork of city and county restrictions
- Rhode Island becomes the first state to transition from total prohibition to regulation in April 2026
- Federal status remains unchanged – kratom is not scheduled but FDA prohibits marketing as supplement
Understanding Kratom’s Federal Legal Status
Kratom remains unscheduled federally. The DEA hasn’t banned it. The Controlled Substances Act doesn’t list it.[1][4]
But that doesn’t mean unrestricted.
The DEA classifies kratom as a “Drug and Chemical of Concern.”[1] This designation signals potential future action. It doesn’t create criminal penalties. It indicates regulatory scrutiny.
The FDA takes a harder stance. They prohibit marketing kratom as a dietary supplement.[1] They ban it as a food additive. They issue warnings about health risks. Liver toxicity concerns them. Seizure potential worries them. Addiction risk drives their position.[1][3]
Federal agencies watch kratom closely. They don’t regulate it uniformly. They create confusion for consumers. They leave enforcement to states.
This federal ambiguity creates problems. States fill the regulatory vacuum. Each develops different approaches. Some ban completely. Others regulate strictly. Many do nothing.
The result? A confusing legal landscape. One that changes frequently. One that requires constant attention.
Complete Kratom Bans: States Where It’s Illegal
Seven states ban kratom entirely.[1] Possession carries serious consequences. These states treat kratom like heroin. Like LSD. Like Schedule I substances.
The Seven Banned States
Alabama maintains a complete prohibition. Alabama classifies kratom as Schedule I. Possession means criminal charges. Distribution brings felony penalties.
Arkansas enforces strict bans. Arkansas law prohibits all kratom products. No exceptions exist. No medical use allowed.
Indiana bans kratom statewide. But change approaches. Legislators introduced KCPA bills.[1] Indiana might shift to regulation. Not yet though.
Louisiana implemented the newest ban. August 1, 2025 marked enforcement.[1] The state became the seventh to prohibit kratom. Recent change caught users off guard.
Vermont prohibits kratom completely. Legislative efforts aim to reverse this.[1] Bills propose KCPA adoption. Current status? Still banned.
Wisconsin enforces total prohibition. Like Vermont, legislative change looms.[1] Wisconsin lawmakers consider KCPA frameworks. Current law remains strict.
Rhode Island currently bans kratom. But April 2026 changes everything.[1] Rhode Island becomes the first state to reverse a ban. They’re adopting regulatory frameworks. Historic shift approaching.
Washington D.C. also maintains complete prohibition. The nation’s capital treats kratom as controlled. Possession brings legal consequences.
Penalties Vary Significantly
Each banned state sets different penalties. Some impose misdemeanor charges. Others pursue felonies. Fines range from hundreds to thousands. Jail time varies widely.
Most users in banned states avoid kratom. The legal risk outweighs benefits. Crossing state lines to purchase works. But transporting back creates problems.
Skip kratom if you live in these states. The legal consequences aren’t worth it. Wait for legislative change. Or relocate to kratom legal states.
Kratom Legal States With Consumer Protection Laws
Twenty-four states regulate kratom through consumer protection laws.[1] These states allow kratom. But they set strict rules. Age restrictions apply. Testing requirements exist. Labeling standards matter.
The Kratom Consumer Protection Act (KCPA)
Most regulatory states adopt KCPA frameworks. This model legislation works. It protects consumers. It ensures product quality.
KCPA states require:
- Minimum age restrictions (18 or 21)
- Third-party testing for contaminants
- Alkaloid concentration limits
- Clear labeling with serving sizes
- Vendor registration and compliance
Age Restrictions Across States
Some states set the minimum at 18. Others require 21. Georgia raised its age to 21 in January 2025.[3] The new law works better. It reduces youth access.
States with age 21 requirements:
- Georgia
- Tennessee
- Utah
- Nevada
States with age 18 requirements:
- Arizona
- North Carolina
- Oklahoma
- Florida
Understanding how old you need to be matters. Vendors check ID. They refuse sales to minors. Penalties for selling to underage buyers run high.
Alkaloid Concentration Limits
The key restriction? 7-hydroxymitragynine caps. Most states limit this alkaloid to 2% of total content.[1] This targets synthetic kratom. It blocks concentrated extracts.
Why 2% matters: Synthetic 7-OH can be 13 times stronger than morphine.[1] Natural kratom rarely exceeds 2%. Concentrated products create overdose risks. They increase addiction potential.
Tennessee exemplifies this approach. Natural kratom? Legal for adults 21+. Synthetic kratom? Banned completely.[1]
Testing and Labeling Requirements
Regulated states demand third-party testing. Labs check for:
- Heavy metals (lead, mercury, arsenic)
- Microbial contamination (salmonella, E. coli)
- Alkaloid content verification
- Adulterants and synthetic additives
Labels must show:
- Serving size recommendations
- Alkaloid percentages
- Batch numbers for traceability
- Expiration dates
- Manufacturer information
Georgia’s new law prohibits kratom in vaping devices.[3] Smart move. Vaping concentrates the alkaloids. It increases health risks.
States With Strong KCPA Frameworks
California regulates kratom through consumer protection. But local bans complicate things. San Diego prohibits kratom despite state legality.[3]
Florida maintains strong protections. Age 18 minimum. Testing requirements. Clear labeling standards.
Nevada enforces age 21 restrictions. Testing standards apply. Quality varies less than unregulated states.
Texas allows kratom with minimal state regulation. But some counties impose restrictions. Check local laws.
These frameworks work. They protect consumers. They ensure quality. They reduce contamination risks.
Quality varies less in KCPA states. Testing catches bad batches. Labeling helps users dose properly. Age restrictions reduce youth access.
Worth noting? KCPA states see fewer kratom-related incidents. Regulation works better than prohibition. Better than no oversight.
Kratom Legal States Without Specific Regulations

Many states allow kratom without specific laws. No bans exist. No KCPA frameworks apply. No testing requirements.
These states offer maximum freedom. But also maximum risk.
Unregulated States Create Challenges
North Carolina permits kratom for adults 18+. No state-level bans apply. No comprehensive consumer protection exists. Advocates push for KCPA adoption.
Iowa remains completely unregulated. As of January 2026, kratom and 7-OH remain unscheduled.[3][4] No state restrictions exist. No testing requirements apply.
Michigan allows kratom without state regulation. Legal for adults. No specific consumer protections.
Missouri permits kratom statewide. No bans. No regulations. Complete freedom.
Illinois maintains legal status without specific kratom laws. Available for purchase. No state oversight.
The Quality Problem
Unregulated states face quality issues. No testing requirements mean contamination risks. Heavy metals slip through. Salmonella appears occasionally. Alkaloid content varies wildly.
Quality varies significantly in these states. Some vendors test voluntarily. Most don’t. Consumers bear the risk.
Smart buyers choose reputable vendors. They request lab reports. They verify third-party testing. They avoid sketchy sources.
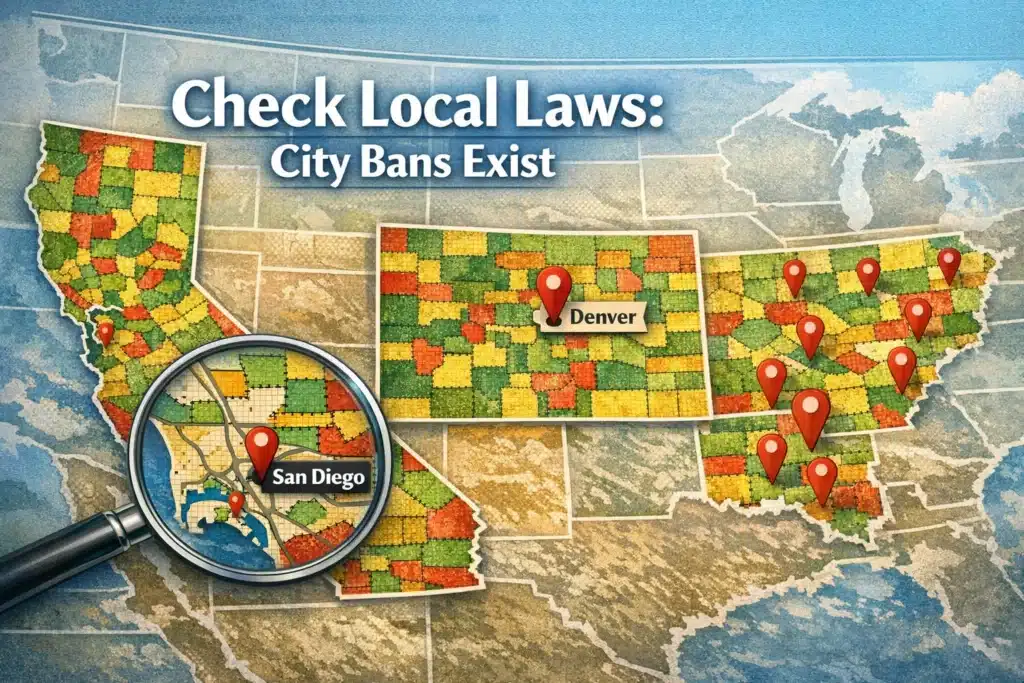
Local Restrictions Within Legal States
Here’s the catch. State legality doesn’t guarantee local access.
Cities and counties impose their own bans.[3] Even in states where kratom remains legal. This creates a patchwork of restrictions.
San Diego, California bans kratom despite state legality.[3] Possession brings local penalties. Sales are prohibited.
Denver, Colorado restricts kratom sales. Colorado allows kratom statewide. But Denver opted out.
Sarasota County, Florida banned kratom. State law permits it. County law prohibits it.
Check local laws always. State legality doesn’t guarantee city permission. County restrictions might apply. Municipal codes vary.
Call local law enforcement. Ask about kratom status. Verify before purchasing. Verify before possessing.
🗺️ Kratom Legal Status Checker 2026
Search your state to find current kratom laws and regulations
State-by-State Kratom Legal Status Reference
Understanding each state’s position helps. Laws change frequently. This reference reflects January 2026 status.
Banned States (Complete Prohibition)
| State | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Banned | Schedule I classification |
| Arkansas | Banned | Complete prohibition |
| Indiana | Banned | KCPA bills introduced[1] |
| Louisiana | Banned | Effective August 1, 2025[1] |
| Rhode Island | Changing | Regulation starts April 2026[1] |
| Vermont | Banned | KCPA bills proposed[1] |
| Wisconsin | Banned | Legislative change considered[1] |
| Washington D.C. | Banned | Complete prohibition |
KCPA Regulated States (24 Total)
These states enforce consumer protection laws:[1]
- Arizona (age 18+)
- Florida (age 18+)
- Georgia (age 21+, effective Jan 2025)[3]
- Nevada (age 21+)
- Tennessee (age 21+, natural only)[1]
- Utah (age 21+)
- And 18 additional states with varying requirements
Unregulated Legal States
North Carolina – Legal, age 18+, no KCPA
Ohio – Legal, no state restrictions
Michigan – Legal, no regulations
Missouri – Legal, unrestricted
Illinois – Legal, no specific laws
New York – Legal, no state bans
Plus approximately 15 other states with similar status.
States With Pending Legislation
Several states consider kratom bills in 2026. Indiana, Vermont, and Wisconsin introduced KCPA adoption measures.[1] These could shift from bans to regulation.
Other states consider new restrictions. Legislative sessions bring changes. Monitor your state’s proposals.
Recent Legislative Changes
Kratom laws evolved significantly in 2025. More changes approach in 2026.
Louisiana’s August 2025 Ban
Louisiana became the seventh banned state.[1] The law took effect August 1, 2025. Users had minimal warning. Vendors scrambled to comply.
The ban surprised many. Louisiana previously allowed kratom. No major incidents prompted the change. Legislative momentum drove prohibition.
This ban doesn’t work well. It criminalizes users. It doesn’t address safety concerns. It pushes consumers to unregulated sources.
Georgia’s Regulatory Overhaul
Georgia’s Kratom Consumer Protection Act took effect January 1, 2025.[3] Major improvements followed.
Key changes:
- Age raised from 18 to 21
- Serving size labels required
- Vaping device prohibition added
- Manufacturer penalties established ($250 to felony charges)[3]
This law works. It protects young adults. It ensures product quality. It maintains legal access.
Rhode Island’s Historic Reversal
April 2026 marks a milestone. Rhode Island transitions from ban to regulation.[1] First state ever to reverse complete prohibition.
The new framework includes:
- KCPA-style consumer protections
- Age restrictions
- Testing requirements
- Vendor licensing
This sets a precedent. Other banned states might follow. Indiana, Vermont, and Wisconsin watch closely.[1]
The KCPA Expansion Trend
More states adopt KCPA frameworks annually. The model works. It balances access with safety.
Twenty-four states now enforce consumer protection laws.[1] That number will likely grow. Legislators see the benefits. Consumers support regulation over prohibition.
Regulation beats prohibition. It ensures quality. It maintains access. It reduces harm.
Federal Developments to Watch
The FDA continues kratom scrutiny. They issue periodic warnings. They cite health concerns. They maintain marketing prohibitions.[1][3]
But federal scheduling remains unlikely. Too much state-level momentum exists. Too many users rely on kratom. Political will for prohibition lacks.
The DEA “Drug of Concern” designation persists.[1] This creates uncertainty. But no immediate scheduling threat exists.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is kratom legal in the United States?
Kratom is legal at the federal level in the United States. However, legality depends on state and local laws. Some states ban kratom entirely, while others allow it with restrictions. Cities and counties can also enforce their own rules, which may differ from state law.
Which states have banned kratom?
A small number of states have banned kratom under controlled substance or consumer protection laws. As of recent updates, bans are commonly reported in states such as Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Wisconsin. Laws can change, so checking current state statutes is important.
Are there states where kratom is legal but regulated?
Yes, several states allow kratom but regulate its sale and labeling. These states often follow consumer safety standards that focus on product quality and age limits. Regulation usually addresses purity, labeling accuracy, and retail compliance rather than personal possession or use.
What is the Kratom Consumer Protection Act?
The Kratom Consumer Protection Act is a state level framework designed to regulate kratom products rather than ban them. It typically sets rules for manufacturing and sales, including requirements related to labeling, product testing, and age restrictions. Adoption varies by state and enforcement differs locally.
Can kratom be illegal in a city even if the state allows it?
Yes, local governments can restrict kratom even when it is legal statewide. These local bans or limits are often based on municipal ordinances. Common examples include restrictions in specific cities or counties that operate independently from state level decisions.
How can someone check if kratom is legal in their state?
- Review the official state legislative website for controlled substance laws
- Check recent state or local government press releases
- Search city or county ordinances related to kratom
- Consult reputable legal or policy tracking sources
Is kratom legal to ship across state lines?
Kratom can be shipped between states where it is legal. Shipping into a state or locality where kratom is banned may violate local laws. Online sellers and buyers are generally expected to follow destination based rules rather than federal guidelines alone.
Do kratom laws change often?
Kratom laws can change due to new legislation or local policy decisions. Updates may occur annually or after public health reviews. Because enforcement and legal status can shift, staying informed through official government sources is recommended for accurate and current information.
Conclusion
Kratom legal states create a complex landscape in 2026. Seven states ban it completely. Twenty-four regulate it through KCPA frameworks. The rest allow it without specific restrictions.
Understanding your state’s laws matters most. Check state regulations. Verify local restrictions. Confirm vendor compliance.
The trend favors regulation over prohibition. Rhode Island reverses its ban in April 2026.[1] Indiana, Vermont, and Wisconsin consider similar moves.[1] More states adopt KCPA frameworks annually.
Quality varies significantly across jurisdictions. KCPA states offer better protection. Testing requirements reduce contamination. Age restrictions limit youth access. Alkaloid caps prevent dangerous concentrations.
References
[1] Kratom Legal Status Professionals – https://foundersfuel.co/blog/kratom-legal-status-professionals
[2] Kratom Ban Update – https://www.quick.md/quick-tips/kratom-ban-update/
[3] Kratom Legal Status – https://pttcnetwork.org/products_and_resources/kratom-legal-status/
[4] Final Kratom And 7 Hydroxymitragynine 7 Oh Federal And Iowa Legal Status – https://pttcnetwork.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/FINAL-Kratom-and-7-Hydroxymitragynine-7-OH-Federal-and-Iowa-Legal-Status.pdf
Daniel Brooks
Daniel Brooks is a U.S. based botanical writer with over six years of hands on experience in kratom focused content. He studies kratom strains, sourcing standards, dosage patterns, and consumer safety topics. He stays up to date with current news, regulatory changes, and market trends related to kratom and botanical products.
His work includes educational guides, strain breakdowns, and vendor reviews written for everyday users. He avoids promotional language and presents clear facts. Daniel helps readers understand both benefits and risks so they can make informed choices about responsible kratom use.
Ryan Mitchell
Ryan Mitchell reviews and approves all kratom and botanical content before it is published. He has worked in the botanical space since 2013 and has been closely involved in kratom education, sourcing standards, and product evaluation.
Ryan actively supports responsible kratom use and spends time engaging with user communities where botanicals are discussed in detail. He has guided tens of thousands of customers through product selection and usage questions over the years. He works directly with trusted growers and suppliers to verify quality. He also ensures third party lab testing is completed so products meet safety and purity expectations before reaching the public.

